Q: Will compostable plastics break down?
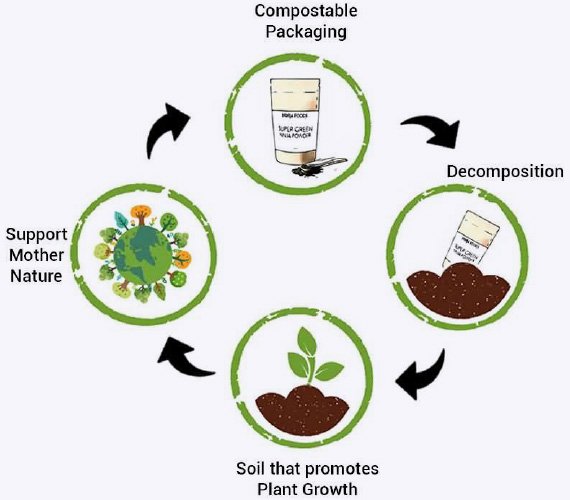
Compostable bio-plastics will break down into soil unlike traditional plastics which last for hundreds of years. Most compostable plastics are intended to be composted in an industrial or commercial composting system, and may take much longer to break down under normal, at-home conditions. It’s also possible that the bag will take much long to break down with your product in it — depending on what your product is.
Q: Are compostable plastic bags freezer safe?
It depends, some materials can be frozen others can become brittle and crack when frozen.
Q: Are compostable plastic bags good for
heated food?
Generally compostable bags are not a good choice for high heat application.
Q: Can you tell the difference between
compostable plastic and regular plastic?
No, compostable plastic and regular plastic look and feel about the same.
Q: How are compostable plastics like PLA made?
Compostable plastics are generally made from a raw material such as corn, sugar cane and starch made from (PLA) polylactic acid and clear cellulose . Currently, the most common raw material uses in PLA is field corn, although other plant sources are being developed. Polylactic acid (PLA) is one of the primary alternatives to traditional oil-based plastics. Polylactic acid is highly popular as a plant-based polymer (a bio-plastic) because its general performance characteristics are similar to many non-compostable polymers and can be processed in similar ways. There are some distinct performance trade-offs that must be considered when using polylactic acid as a laminate element in flexible barrier packaging, but with continued technological advancements many of these limitations are being overcome. Below is a example of a bio-plastic bottle disintegrating under composting condition.
Q: What are compostable bags made from?
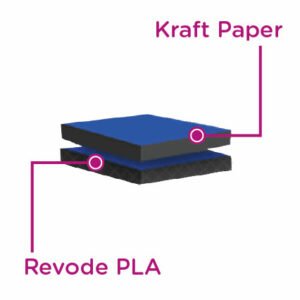
Polylactic Acid is principally made through two different processes —condensation and polymerization. The most common polymerization technique is known as ring-opening polymerization. This is a process that utilizes metal catalysts in combination with lactide to create the larger polylactic acid molecules. The condensation process is similar with the principal difference being the temperature during the procedure and the by-products (condensates) that are released because of the reaction. Here are some the reasons why biodegradable and compost barrier packaging made of PLA is a great choice for many applications.
Q: Can high barrier compostable plastic bags be produced?
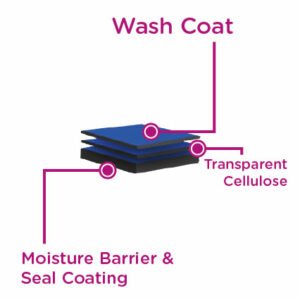
The primary drawback of compostable materials like PLA is that it is a relatively low barrier material. PLA must be further processed or coated for use with liquids or products that require a higher MVTR (moisture vapor transition rate) barrier rating because uncoated PLA has a high-water vapor permeability. The primary solution to these limitations is to coat the PLA layer with additional elements. The most common MVTR boosters are coatings are: Aluminum Oxide, Silicon Oxide, and PVDC.
They are certified compostable by the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI), petroleum-free and registered as USDA Bio-based Products. It is a cost-effective barrier that has been used for granola, candy, chips, cosmetics, jerky, pharmaceuticals, powders, and many other products.
Q: Can compostable plastic be used as a barrier film?
PLA can be processed into either a COEX or Biaxially oriented film (BOPLA). BOPLA is the most common form of film used for flexible packaging as a barrier film. PLA based compostable plastic bags can specifically replace PET, and biax PP film layers for many application. When PLA is laminated to a paper it can create a more durable packaging solution than when PLA is cross laminated to itself.
Q: What are biodegradable bags made from?
These bag are made from bio-plastics, which are plastics produced using renewable raw plant materials. Most of the materials we sell that are biodegradable are made of some combination of sugar cane, beets, and other starchy plants. Regular plastic is made with petroleum-based plastics and occasionally combined with other materials. With biodegradable plastic bags, you get a substance produced using renewable resources.
Q: Are compostable bags the same as biodegradable bags?
Compostable is a subset of of biodegradable and as far as packaging is concerned these are very similar terms. Home composting refers to packaging that can be composted (biodegrade) under ambient conditions, while the more general “OK compost” may refer to industrial composting conditions, (solid waste facilities)
Q: What’s the difference between bio-based plastics and biodegradable plastic?
“Bio-Based Plastics”, and “biodegradable plastic” are phrases that represent two different attributes, but the two terms, bio-based and biodegradable, are often used in conjunction with one another. When the terms are paired as modifiers with the term plastics, the phrase bio-based and biodegradable plastics denotes a composition deriving from mainly natural substances that break down over time, with the environment, the materials’ composition, and the time-frame all factoring in how quickly the break-down occurs.
Bio-based and biodegradable plastics are relatively new plastic materials to be used by the food packaging industries. As these newer bio-plastics degrade, they emit a very low amount of carbon, so they leave a very low carbon footprint. They are overall much more environmentally friendly than conventional plastics. Because these materials are much less harmful to the environment than fossil-based plastics, their use has been on the rise.
Small amounts of fossil-based plastics are still used in making some bio-based and biodegradable plastics, but the amount of petroleum plastic used in making bio-based and biodegradable plastics continues to be reduced with the invention of new polymers. As a result, bio based and biodegradable plastics leave significantly less plastic waste to damage the environment than do fossil-based plastics, and the amount of time required to decompose is reduced to three to six months instead of decades to hundreds of years or more.
Types of bio-based and biodegradable polymers are polylactic acid (PLA), biodegradable starch-based plastics, cellophane, biodegradable and bio-based polyesters, drop-in bio-based materials, polyethyline furanoate (PEF) and others. New bio-based and biodegradable polymers are under development including PBS.